
Nerve conduction testing takes 15 minutes to an hour or more, depending upon how many areas are studied. Nerve conduction studies are usually done before an EMG if both tests are being done. The corresponding nerves on the other side of the body may be studied for comparison.

The speed of the response is called the conduction velocity. The time it takes the muscle to contract in response to the electrical pulse is recorded. Each pulse is very brief (less than a millisecond). Keep in mind that only a very low-voltage electrical current is used. The testing can be quite uncomfortable and makes some people nervous. It feels like the tingling you feel when you rub your feet on the carpet then touch a metal object. You will feel a brief, burning pain, a tingling sensation and a twitching of the muscle when the electrical pulse is applied. Several, brief electrical pulses are sent to the nerve. A recording electrode is placed over the muscles supplied by that nerve. A shock-emitting electrode is placed directly over the nerve to be studied. In a nerve conduction study, several flat metal disc electrodes are taped or pasted to your skin.

Help diagnose nerve disorders, such as carpal tunnel syndrome or Guillain-Barré syndrome.Find and evaluate damage to all the nerves that lead away from the brain and spinal cord to the smaller nerves that branch out from them.The study can show where there is a blockage of the nerve pathway.
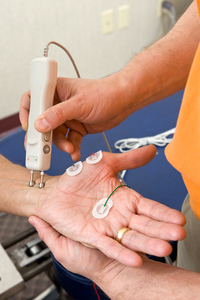
The nerve conduction study stimulates specific nerves and records their ability to send the impulse to the muscle. About spinal diagnostics: nerve conduction studiesĪ nerve conduction study is usually done along with electromyography (EMG).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
